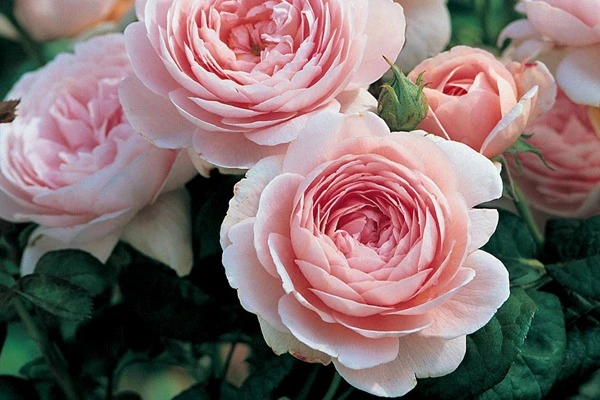

Rose Plant Care: A to Z Guide
Roses are among the most cherished flowers in the world. They symbolize love, beauty, and elegance. However, growing and maintaining a healthy rose plant requires proper care and attention. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced gardener, this A-to-Z guide will help you nurture your rose plants effectively.
Good air circulation is crucial for preventing fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and black spots. Space your rose plants properly and prune them regularly.
Roses thrive in well-draining, loamy soil enriched with organic matter. The ideal pH range is between 6.0 and 6.5.
Adding compost to your soil enhances fertility and improves moisture retention. It also provides essential nutrients for healthy plant growth.
Ensure that the planting area has good drainage to prevent root rot. If necessary, plant roses in raised beds.
Roses require at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Choose a location with full sun exposure.
Feed your roses with a balanced fertilizer (e.g., 10-10-10) every 4-6 weeks during the growing season. Organic fertilizers like bone meal and fish emulsion are also beneficial.
Many roses are grafted onto rootstocks to improve disease resistance and growth. Choose grafted roses if you want robust and disease-resistant plants.
Too much humidity can encourage fungal diseases. Ensure proper spacing and air circulation to keep humidity levels in check.
Common pests like aphids, spider mites, and thrips can harm rose plants. Use neem oil, insecticidal soap, or introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs to control them naturally.
These pests can damage rose leaves and flowers. Hand-pick them off your plants or use traps to reduce their population.
Weeds compete with roses for nutrients and water. Mulching helps suppress weeds while keeping the soil moist.
Monitor leaves for signs of disease or pest infestation. Yellowing or black spots may indicate fungal infections or nutrient deficiencies.
A layer of mulch (2-3 inches) around the base of the plant helps retain moisture, regulate soil temperature, and prevent weed growth.
Essential nutrients for roses include nitrogen (for leaf growth), phosphorus (for root development), and potassium (for flower production).
Using organic fertilizers and pesticides keeps your rose garden chemical-free and eco-friendly.
Regular pruning removes dead or weak stems, improves air circulation, and encourages new growth. Prune in early spring before new growth begins.
Water deeply but infrequently. Roses need about 1-2 inches of water per week. Avoid overhead watering to prevent fungal diseases.
If growing roses in containers, repot them every 2-3 years with fresh soil to provide adequate nutrients and space for growth.
Adjust care routines based on the season. In summer, provide extra water; in winter, protect roots with mulch.
Use trellises or support structures to train climbing roses and encourage vertical growth.
Choose the right variety for your garden—hybrid teas, floribundas, grandifloras, climbers, or shrub roses—based on your climate and preferences.
Watch out for common rose diseases like black spot, powdery mildew, and rust. Remove affected leaves and apply fungicides when necessary.
In colder climates, cover the base of the plant with mulch, straw, or burlap to protect it from frost damage.
Some rose varieties, like Rugosa roses, are drought-tolerant and can be used in xeriscaping (low-water gardening).
Regular maintenance throughout the year ensures healthy and beautiful roses. Keep up with watering, feeding, and pruning.
Minimize the use of synthetic chemicals and opt for natural fertilizers, compost, and biological pest control methods.
Caring for roses may seem daunting at first, but with the right knowledge and routine, you can grow stunning, healthy roses. Follow this A-to-Z guide, and your garden will flourish with beautiful blooms all season long!
Happy Gardening!